Bunion/Hallux Valgus
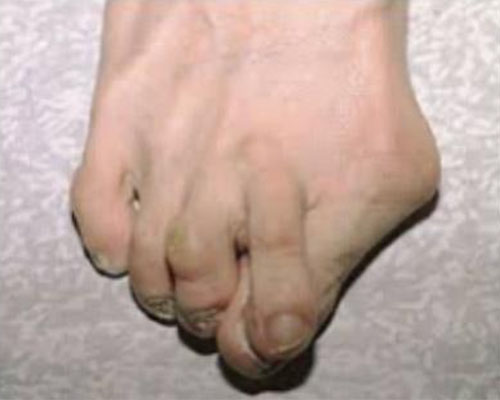
Bunion Hallux Valgus is the deformity of great toe in which it deviates towards the lesser toes and the joints between the toe and foot becomes prominent, red and painful. On common man’s it has been called as bunion meaning bony prominence of inner aspect of base of hallux. But it is a misnomer.
It’s a complex deformity involving not only the great toe but also other toe and foot bone. Most of the time it is associated with hammer toe deformity of the second toe, metatarsalgia, callosities over the interphalangeal joint of the second toe and plantar aspect of other metatarsal heads.
Hallux valgus occurs in all age groups and gender with higher prevalence in females. There is a strong familial predilection, nearly 70% of Bunion Hallux Valgus has a family history. It can be seen among siblings and descend among generations.
Bunion Hallux Valgus has two form of presentation
- Adult onset hallux valgus: In this variety one does not show any deformity at childhood but develops later on, which is gradually progressive.
- Juvenile hallux valgus: In this variety deformity presents since birth and usually not progressive.
There are few risk factors for developing bunion hallux valgus. Most of these factors are intrinsic, means there are some inbuilt structural abnormalities present which determines the development of bunion hallux valgus, like
- Inappropriate length of metatarsals
- Round shape of metatarsal head
- Misaligned metatarsals
- Flat foot
- Tight calf muscle
- Ligamentous laxity
- Rheumatoid arthritis
The extrinsic factors are
- Prolonged use of high heel and narrow toe box shoe
- Pain and tenderness in and around big toe
- Callus and corn formation at medial side of great toe ball of toe and at bunion site
- Hammer toe and crossover toe deformity
- Difficulty in walking and wearing shoe
Severe Hallux Valgus deformity foot associated with crossover, Hallux deformity foot and hammer toe deformity, callosities and bunion
If your deformity is progressing, becomes painful and is associated with restriction of daily activity like walking, wearing specific shoes or there is painful corns and callus formation you should visit a specialist Foot & Ankle surgeon.
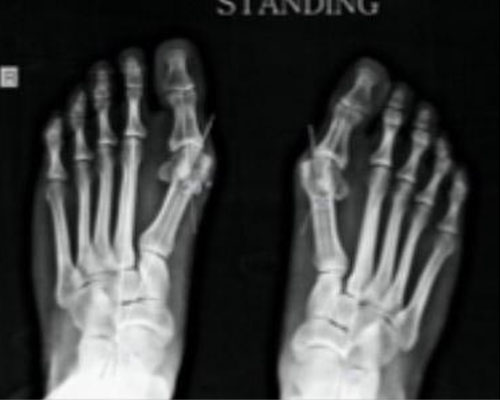
Your doctor will do a detailed clinical examination to estimate the severity of deformity and associated secondary effect on gait, local skin and other toes along with justification of your symptom affecting your day to day life. He will advise for a weight bearing x-ray of your foot for radiological evaluation of joints affected and grading of deformity. Other than x-ray, foot pressure scan and 3D foot scan is helpful in detection of deformity and abnormal pressure point, required in custom made insole and orthotic design.
Treatment of hallux valgus is mainly conservative. Cosmetic correction of deformity is not recommended until it is symptomatic. Only symptomatic like pain and unable to use shoe and walk due to deformity and severe deformity in juvenile hallux valgus are recommended for surgical correction.
Conservative:
- NSAIDs, local analgesic, over the counter pain medication and icing to help pain relief
- Modified footwear- Shoe with wider toe box and extra recesses in insole for toes
- Orthotics- Custom made shoe inserts, toe separator, bunion splint etc
- Padding- Over the counter silicone bunion pad or custom made bunion pad acts as buffer between your shoe and feet
Surgical:
Two types of surgeries are being done
- For non-arthritic bunion hallux valgus: deformity correction of hallux joint with osteotomy, soft tissue release and augmentation and associated lesser toe deformity correction.
- For arthritic bunion hallux valgus: hallux valgus deformity foot correction with arthrodesis/fusion of hallux joint and associated lesser toe deformity correction.
In addition, hallux valgus and flat feet correction and recession of gastrocnemius is also done if required.
